282 : Incompressible MHD
This example yields a prototype for te stationary incompressible viscious MHD equations that seek a velocity field $\mathbf{u}$, a pressure field $p$ and a divergence-free magnetic field $\mathbf{B}$ such that
\[\begin{aligned} - \mu \Delta \mathbf{u} + \nabla \cdot (\mathbf{u} \otimes \mathbf{u} - \mathbf{B} \otimes \mathbf{B}) + \nabla (p + \frac{1}{2} \mathbf{B} \cdot \mathbf{B}) & = 0\\ \mathrm{div}(\mathbf{u}) & = 0\\ - \eta \Delta \mathbf{B} + \nabla \cdot (\mathbf{u} \otimes \mathbf{B} - \mathbf{B} \otimes \mathbf{u}) & = 0\\ \mathrm{div}(\mathbf{B}) & = 0\\ \end{aligned}\]
on a rectangular 2D domain. Here, $\mu$ and $\eta$ are the viscosity and resistivity of the fluid and the magnetic field, respectively.
module Example282_IncompressibleMHD
using ExtendableFEM
using ExtendableGrids
using LinearAlgebra
function f!(result, qpinfo)
result .= 0
end
function g!(result, qpinfo)
x = qpinfo.x
result[1] = sin(2*pi*x[2])*cos(pi*x[1])
result[2] = 0
end
function kernel_nonlinear!(result, u_ops, qpinfo)
u, B, ∇u, ∇B, p, q = view(u_ops, 1:2), view(u_ops, 3:4), view(u_ops, 5:8), view(u_ops, 9:12), view(u_ops, 13), view(u_ops, 14)
μ = qpinfo.params[1]
η = qpinfo.params[2]
# viscous terms and pressures
result[5] = μ * ∇u[1] - p[1]
result[6] = μ * ∇u[2]
result[7] = μ * ∇u[3]
result[8] = μ * ∇u[4] - p[1]
result[9] = η * ∇B[1] - q[1]
result[10] = η * ∇B[2]
result[11] = η * ∇B[3]
result[12] = η * ∇B[4] - q[1]
# Lorentz force
result[1] = - dot(B, view(∇B,1:2))
result[2] = - dot(B, view(∇B,3:4))
BdotB = (B[1]*B[1] + B[2]*B[2])/2
result[5] -= BdotB
result[8] -= BdotB
# convection term for u and B
result[1] += dot(u, view(∇u,1:2))
result[2] += dot(u, view(∇u,3:4))
result[3] = dot(u, view(∇B,1:2)) - dot(B, view(∇u,1:2))
result[4] = dot(u, view(∇B,3:4)) - dot(B, view(∇u,3:4))
# divergence constraint
result[13] = -(∇u[1] + ∇u[4])
result[14] = -(∇B[1] + ∇B[4])
return nothing
end
# everything is wrapped in a main function
function main(; Plotter = nothing, μ = 1e-3, η = 1e-1, nrefs = 5, kwargs...)
# load grid (see function below)
xgrid = uniform_refine(grid_unitsquare(Triangle2D), nrefs)
# problem description
PD = ProblemDescription()
u = Unknown("u"; name = "velocity")
B = Unknown("B"; name = "magnetic field")
p = Unknown("p"; name = "pressure")
q = Unknown("q"; name = "magnetic pressure")
assign_unknown!(PD, u)
assign_unknown!(PD, B)
assign_unknown!(PD, p)
assign_unknown!(PD, q)
assign_operator!(PD, NonlinearOperator(kernel_nonlinear!, [id(u), id(B), grad(u), grad(B), id(p), id(q)]; bonus_quadorder = 2, params = [μ,η], kwargs...))
assign_operator!(PD, LinearOperator(f!, [id(u)]))
assign_operator!(PD, LinearOperator(g!, [id(B)]))
assign_operator!(PD, HomogeneousBoundaryData(u; regions = 1:4))
assign_operator!(PD, HomogeneousBoundaryData(B; regions = [1]))
assign_operator!(PD, FixDofs(p; dofs = [1]))
assign_operator!(PD, FixDofs(q; dofs = [1]))
# P2-bubble finite element method
FETypes = [H1P2{2, 2}, H1P2{2, 2}, H1P1{1}, H1P1{1}]
# generate FESpaces and Solution vector
FES = [FESpace{FETypes[j]}(xgrid) for j = 1:4]
# solve
sol = ExtendableFEM.solve(PD, FES; target_residual = 1e-8, time = 0, kwargs...)
# plot
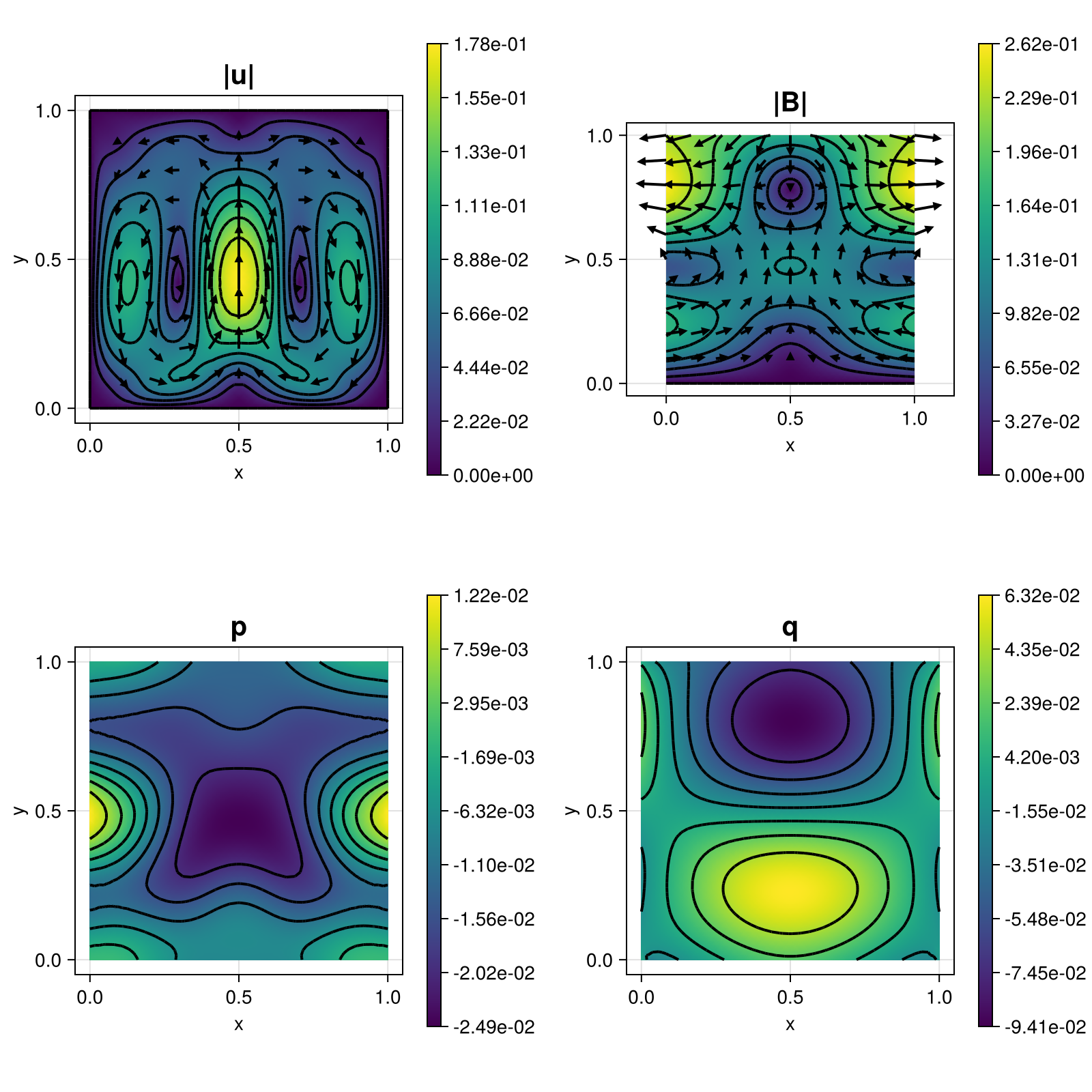
plt = plot([id(u), id(B), id(p), id(q)], sol; Plotter = Plotter)
return sol, plt
end
endThis page was generated using Literate.jl.