222 : Pressure-robustness 2D
This example studies two benchmarks for pressure-robust discretisations of the stationary Navier-Stokes equations that seek a velocity $\mathbf{u}$ and pressure $\mathbf{p}$ such that
\[\begin{aligned} - \mu \Delta \mathbf{u} + (\mathbf{u} \cdot \nabla) \mathbf{u} + \nabla p & = \mathbf{f}\\ \mathrm{div}(u) & = 0 \end{aligned}\]
with (possibly time-dependent) exterior force $\mathbf{f}$ and some viscosity parameter $\mu$.
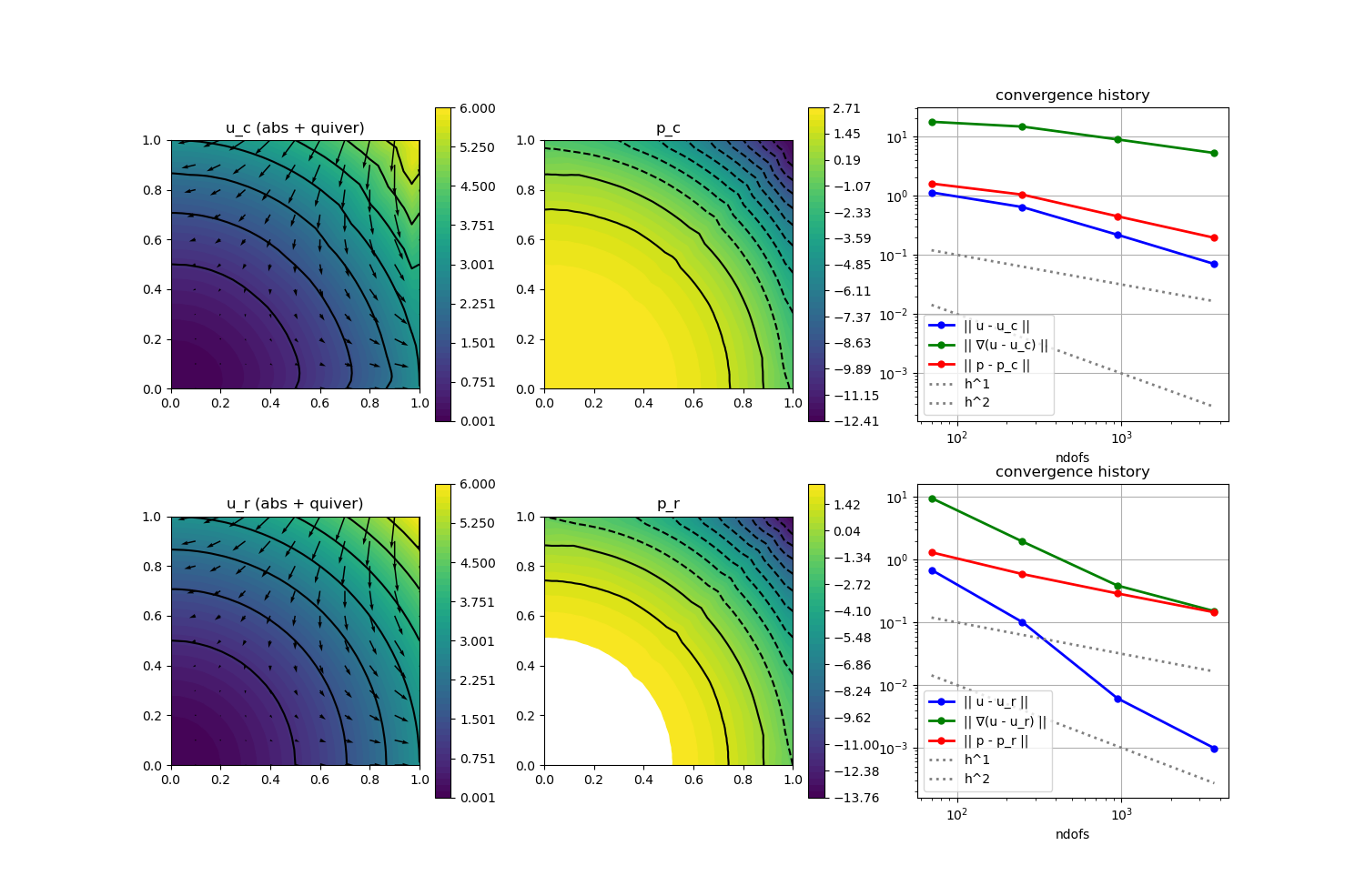
Pressure-robustness is concerned with gradient forces that may appear in the right-hand side or the material derivative and should be balanced by the pressure (as divergence-free vector fields are orthogonal on gradient fields). Here, two test problems are considered:
- HydrostaticTestProblem() : Stokes (without convection term) and $\mathbf{f} = \nabla p$ such that $\mathbf{u} = 0$
- PotentialFlowTestProblem() : Navier-Stokes with $\mathbf{f} = 0$ and $\mathbf{u} = \nabla h$ for some harmonic function
In both test problems the errors of non-pressure-robust discretisations scale with $1/\mu$, while the pressure-robust discretisation solves $\mathbf{u} = 0$ exactly in test problem 1 and gives much better results in test problem 2.
module Example222_PressureRobustness2D
using GradientRobustMultiPhysics
using ExtendableGrids
using GridVisualize
# problem data
function HydrostaticTestProblem()
# Stokes problem with f = grad(p)
# u = 0, p = x^3+y^3 - 1//2
function P1_pressure!(result,x)
result[1] = x[1]^3 + x[2]^3 - 1//2
end
u = DataFunction([0,0]; xdim = 2, name = "u")
p = DataFunction(P1_pressure!, [1,2]; name = "p", dependencies = "X", bonus_quadorder = 3)
f = ∇(p)
return p,u,∇(u),f,false
end
function PotentialFlowTestProblem()
# NavierStokes with f = 0
# u = grad(h) with h = x^3 - 3xy^2
# p = - |grad(h)|^2 + 14//5
function P2_pressure!(result,x)
result[1] = - 1//2 * (9*(x[1]^4 + x[2]^4) + 18*x[1]^2*x[2]^2) + 14//5
end
function P2_velo!(result,x)
result[1] = 3*x[1]^2 - 3*x[2]^2;
result[2] = -6*x[1]*x[2];
end
u = DataFunction(P2_velo!, [2,2]; name = "u", dependencies = "X", bonus_quadorder = 2)
p = DataFunction(P2_pressure!, [1,2]; name = "p", dependencies = "X", bonus_quadorder = 4)
f = DataFunction([0,0]; name = "f")
return p,u,∇(u),f,true
end
function solver(Problem, xgrid, FETypes, viscosity = 1e-2; nlevels = 4, target_residual = 1e-10, maxiterations = 20, Plotter = nothing)
# load problem data and set solver parameters
ReconstructionOperator = FETypes[3]
p,u,∇u,f,nonlinear = Problem()
# setup classical (Problem) and pressure-robust scheme (Problem2)
Problem = IncompressibleNavierStokesProblem(2; viscosity = viscosity, nonlinear = false)
add_boundarydata!(Problem, 1, [1,2,3,4], BestapproxDirichletBoundary; data = u)
Problem2 = deepcopy(Problem)
Problem.name = "Stokes problem (classical)"
Problem2.name = "Stokes problem (p-robust)"
# assign right-hand side
add_rhsdata!(Problem, 1, LinearForm(Identity, f))
add_rhsdata!(Problem2, 1, LinearForm(ReconstructionOperator, f))
# assign convection term
if nonlinear
add_operator!(Problem,[1,1], ConvectionOperator(1, Identity, 2, 2))
add_operator!(Problem2,[1,1], ConvectionOperator(1, ReconstructionOperator, 2, 2; test_operator = ReconstructionOperator))
end
# define bestapproximation problems
BAP_L2_u = L2BestapproximationProblem(u; bestapprox_boundary_regions = [1,2,3,4])
BAP_L2_p = L2BestapproximationProblem(p; bestapprox_boundary_regions = [])
BAP_H1_u = H1BestapproximationProblem(∇u, u; bestapprox_boundary_regions = [1,2,3,4])
# define ItemIntegrators for L2/H1 error computation
L2Error_u = L2ErrorIntegrator(u, Identity)
L2Error_p = L2ErrorIntegrator(p, Identity)
H1Error_u = L2ErrorIntegrator(∇u, Gradient)
Results = zeros(Float64, nlevels, 9)
NDofs = zeros(Int, nlevels)
# loop over refinement levels
Solution, Solution2 = nothing, nothing
for level = 1 : nlevels
# uniform mesh refinement
xgrid = uniform_refine(xgrid)
# get FESpaces
FES = [FESpace{FETypes[1]}(xgrid), FESpace{FETypes[2]}(xgrid; broken = true)]
# solve both problems
Solution = solve(Problem, FES; maxiterations = maxiterations, target_residual = target_residual, anderson_iterations = 5)
Solution2 = solve(Problem2, FES; maxiterations = maxiterations, target_residual = target_residual, anderson_iterations = 5)
# solve bestapproximation problems
BA_L2_u = FEVector("Πu",FES[1])
BA_L2_p = FEVector("πp",FES[2])
BA_H1_u = FEVector("Su",FES[1])
solve!(BA_L2_u, BAP_L2_u)
solve!(BA_L2_p, BAP_L2_p)
solve!(BA_H1_u, BAP_H1_u)
# compute L2 and H1 errors and save data
NDofs[level] = length(Solution.entries)
Results[level,1] = sqrt(evaluate(L2Error_u,Solution[1]))
Results[level,2] = sqrt(evaluate(L2Error_u,Solution2[1]))
Results[level,3] = sqrt(evaluate(L2Error_u,BA_L2_u[1]))
Results[level,4] = sqrt(evaluate(L2Error_p,Solution[2]))
Results[level,5] = sqrt(evaluate(L2Error_p,Solution2[2]))
Results[level,6] = sqrt(evaluate(L2Error_p,BA_L2_p[1]))
Results[level,7] = sqrt(evaluate(H1Error_u,Solution[1]))
Results[level,8] = sqrt(evaluate(H1Error_u,Solution2[1]))
Results[level,9] = sqrt(evaluate(H1Error_u,BA_H1_u[1]))
end
# print convergence history
print_convergencehistory(NDofs, Results[:,1:3]; X_to_h = X -> X.^(-1/2), ylabels = ["||u-u_c||", "||u-u_r||", "||u-Πu||"])
print_convergencehistory(NDofs, Results[:,4:6]; X_to_h = X -> X.^(-1/2), ylabels = ["||p-p_c||", "||p-p_r||", "||p-πp||"])
print_convergencehistory(NDofs, Results[:,7:9]; X_to_h = X -> X.^(-1/2), ylabels = ["||∇(u-u_c)||", "||∇(u-u_r)||", "||∇(u-Su)||"])
# plot
p = GridVisualizer(; Plotter = Plotter, layout = (2,3), clear = true, resolution = (1500,1000))
scalarplot!(p[1,1],xgrid,view(nodevalues(Solution[1]; abs = true),1,:), levels = 7)
vectorplot!(p[1,1],xgrid,evaluate(PointEvaluator(Solution[1], Identity)), spacing = 0.1, clear = false, title = "u_c (abs + quiver)")
scalarplot!(p[1,2],xgrid,view(nodevalues(Solution[2]),1,:), levels = 11, title = "p_c")
scalarplot!(p[2,1],xgrid,view(nodevalues(Solution2[1]; abs = true),1,:), levels = 7)
vectorplot!(p[2,1],xgrid,evaluate(PointEvaluator(Solution2[1], Identity)), spacing = 0.1, clear = false, title = "u_r (abs + quiver)")
scalarplot!(p[2,2],xgrid,view(nodevalues(Solution2[2]),1,:), levels = 11, title = "p_r")
convergencehistory!(p[1,3], NDofs, Results[:,[1,7,4]]; add_h_powers = [1,2], X_to_h = X -> X.^(-1/2), ylabels = ["|| u - u_c ||", "|| ∇(u - u_c) ||", "|| p - p_c ||"])
convergencehistory!(p[2,3], NDofs, Results[:,[2,8,5]]; add_h_powers = [1,2], X_to_h = X -> X.^(-1/2), ylabels = ["|| u - u_r ||", "|| ∇(u - u_r) ||", "|| p - p_r ||"])
# return last L2 error of p-robust method for testing
return Results[end,2]
end
# everything is wrapped in a main function
function main(; problem = 2, verbosity = 0, nlevels = 4, viscosity = 1e-2, Plotter = nothing)
# set log level
set_verbosity(verbosity)
# set problem to solve
if problem == 1
Problem = HydrostaticTestProblem
elseif problem == 2
Problem = PotentialFlowTestProblem
else
@error "No problem defined for this number!"
end
# set grid and problem parameters
xgrid = grid_unitsquare(Triangle2D) # initial grid
# choose finite element discretisation
#FETypes = [H1BR{2}, L2P0{1}, ReconstructionIdentity{HDIVRT0{2}}] # Bernardi--Raugel with RT0 reconstruction
FETypes = [H1BR{2}, L2P0{1}, ReconstructionIdentity{HDIVBDM1{2}}] # Bernardi--Raugel with BDM1 reconstruction
#FETypes = [H1CR{2}, L2P0{1}, ReconstructionIdentity{HDIVRT0{2}}] # Crouzeix--Raviart with RT0 reconstruction
# run
solver(Problem, xgrid, FETypes, viscosity; nlevels = nlevels, Plotter = Plotter)
return nothing
end
# test function that is called by test unit
# tests if hydrostatic problem is solved exactly by pressure-robust methods
function test(; Plotter = nothing)
xgrid = uniform_refine(grid_unitsquare_mixedgeometries())
testspaces = [[H1CR{2}, L2P0{1}, ReconstructionIdentity{HDIVRT0{2}}],
[H1BR{2}, L2P0{1}, ReconstructionIdentity{HDIVRT0{2}}],
[H1BR{2}, L2P0{1}, ReconstructionIdentity{HDIVBDM1{2}}]
]
error = []
for FETypes in testspaces
push!(error, solver(HydrostaticTestProblem, xgrid, FETypes, 1; nlevels = 1))
println("FETypes = $FETypes error = $(error[end])")
end
xgrid = uniform_refine(grid_unitsquare(Triangle2D))
testspaces = [
[H1P2B{2,2}, H1P1{1}, ReconstructionIdentity{HDIVRT1{2}}]
]
error = []
for FETypes in testspaces
push!(error, solver(HydrostaticTestProblem, xgrid, FETypes, 1; nlevels = 1, Plotter = Plotter))
println("FETypes = $FETypes error = $(error[end])")
end
return maximum(error)
end
endThis page was generated using Literate.jl.